Soil Health is important for all land users from large scale producers to hobby producers. The USDA Natural Resource Conservation Services (NRCS) is a vital source of information on the topic of soil quality. The Indiana State Department of Agriculture (ISDA), Conservation Cropping Systems Initiative (CCSI) and Purdue University are additional sources of information on soil quality, as well as other agriculture news from across the state. The Purdue Extension Office has a publication about Collecting Soil Samples for Testing to guide landowners and producers in the collection of soil samples for testing before applying fertilizer and other nutrients. There is also a Soil Sampling for Nutrient Management brochure from the USDA NRCS.
For further soil sampling and testing guidance, please see our Soil Sampling and Analysis page.

What is soil health?
Soil health is “the continued capacity of soil to function as a vital living ecosystem that sustains plants, animals, and humans.”
Soil health is protected and enhanced by creating the conditions in the garden or farm for natural biological processes to occur. In natural (ecological) systems, organic matter is maintained, water is conserved, nutrients are cycled, and biological activity thrives.
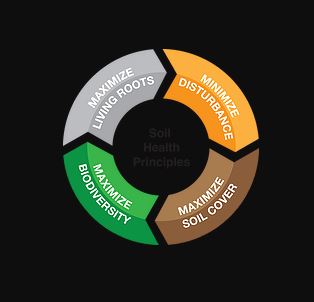
Soil Health Principles
The soil health system is founded on four core principles, which motivate specific conservation practices. These principles create a recipe for regenerating soil health. Keep in mind that all four principles work together as a system; growers will achieve maximum soil health benefits when all four are in practice.
- Minimize disturbance
- Maximize soil cover
- Maximize biodiversity
- Maximize living roots

Benefits of Soil Health
When growers are practitioners of the four principles of soil health, there are many positive results. Good soil health benefits both people and the land. Key improvements include:
- Increased plant health
- Increased plant productivity
- Increased soil organic matter
- Increased water holding capacity
- Increased soil aggregate stability
- Increased water infiltration
- Improved nutrient use efficiency
- Enhanced and diversified soil biology
- Reduced weed pressure
- Reduced pest pressure
What conservation practices can help improve soil health?
Conservation practices are methods growers can use to put the four soil health principles into action on the ground. These practices are a suite of strategies that regenerate soil heath and include:
- Cover crops
- Cover Crops: When, Why, and How? booklet (Please contact the SWCD office if you would like a physical copy of this important resource.)
- Crop rotation
- Mulching
- Native and targeted plantings for beneficial insects and pollinators
- No-till or Reduced-Till
- Nutrient management
Pictures used with permission from Jordan Beehler and CCSI
Educational hyperlinks provided by NRCS